2016 год № 4
Внутренние болезни
2Дальневосточный государственный медицинский университет, 680000, ул. Муравьева-Амурского, 35, ул. Муравьева-Амурского, 35, тел. 8-(4212)-76-13-96, e-mail: nauka@mail.fesmu.ru;
3Институт повышения квалификации специалистов здравоохранения, г. Хабаровск
Резюме:
Ключевые слова:
2Far Eastern State Medical University;
3Postgraduate Institute for Public Health Workers, Khabarovsk
Summary:
Key words:
Introduction |
 |
 |
Recent data for the global burden of disease reflect major demographic and lifestyle changes, leading to a rise in non-communicable diseases. Most countries with high levels of tuberculosis (TB) face a large comorbidity burden from both non-communicable and communicable diseases. As the World Health Organization (WHO) and the International Organization against TB and Lung Disease raised a cooperation framework in 2011, which proposed merger care and disease control in diabetic patients with TB, encouraging collaborative research and bidirectional screening for two diseases, the relationship between diabetes and TB or synergies caused more and more concern [1, 2]. Both diabetes and TB are severe chronic diseases. They could outset simultaneously and motivate each other as well. The traditional specific therapeutic methods have failed in management and control of these diseases [3]. Most studies have proposed that diabetes is one of the important risk factors for TB. Diabetes can not only lead to more severe mycobacterium infection, high mortality and low cure rate, but also can lead to a recurrence and reproduce of TB [4, 5]. However, there is less research on TB merger pre-diabetes and diabetes, especially the lack of effective methods in disease control and treatment. Therefore, concerted therapy method is urgently needs for this situation. The need for sustained and increased funding for these initiatives is greater than ever and requires increased research commitment.
The prevalence of pre-diabetes and diabetes is 9,7 % and 15,5 %, respectively in China [6]. Among 3017 people in Nangang district of Harbin in Heilongjiang province, the prevalence for pre-diabetes is 3,75 %, and for diabetes is 10,21 % [7]. All data above is the study of natural populations. According to the diagnostic criteria for diabetes in China (1999 WHO diagnostic criteria), all TB patients will be classified as TB patients, TB patients combined pre-diabetes and TB patients combined diabetes. We investigate the prevalence of TB combined with pre-diabetes or diabetes, providing the theoretical basis of TB and diabetes interaction, which would be helpful to control TB and reduce mortality.
Materials and methods
|
 |
 |
Study Population
To analyze the incidence of TB in Heilongjiang province, we investigated the cases of TB patients from 2001-2011, the data of which is from Heilongjiang province hospital. Random collected 421 clinical TB cases of March ~ May 2011 from Heilongjiang province hospital, and weed out the cases below normal blood glucose levels, then 404 cases are included in this study. According to the diagnostic criteria for diabetes in China (1999 WHO diagnostic criteria), all TB patients will be classified as three group, single TB patients group with blood glucose 3,9~6,1 mmol/L, TB patients combined pre-diabetes group with blood glucose 6,1~7,0 mmol/L, and TB patients combined diabetes group with blood glucose more than 7,0 mmol/L.
Statistical Analysis
SPSS16.0 statistical software is applied to processed all data. The prevalence of TB patients combined pre-diabetes or diabetes are analyzed with 95 % confidence intervals (95 % CI).
Ethical Support
All information collected in this study have approved by infectious hospital of Heilongjiang province and Harbin Medical University ethics committee.
Results
|
 |
 |
Case numbers of TB and pulmonary TB in Heilongjiang province
To analyze the prevalence of TB in Heilongjiang province, we first collect TB cases from 2001-2011 in Heilongjiang province hospital. As shown in Figure 1, the numbers of TB cases increase gradually since 2001, and fall slightly at 2011, but still at a high level. Pulmonary TB is the most important composition of TB, and its incidence trend is the similar to TB, also raise gradually from 2001~2011.
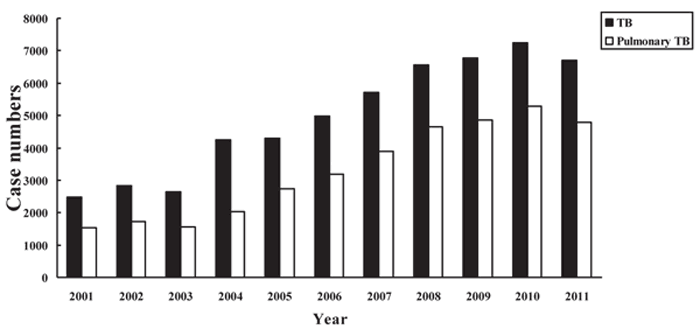
Figure 1. The case numbers of TB and pulmonary TB from 2001~2011
Prevalence of single TB patients, TB patients combined pre-diabetes, and TB patients combined diabetes
Total 404 TB patients cases, 264 cases of male and 140 cases of female, are collected in this study, with an average age of 42,02±17,518. According to the fasting blood glucose levels, all TB patients will be classified as three group, single TB patients group with blood glucose 3,9~6,1 mmol/L, TB patients combined pre-diabetes group with blood glucose 6,1~7,0 mmol/L, and TB patients combined diabetes group with blood glucose more than 7,0 mmol/L. We investigate the prevalence of TB combined with pre-diabetes or diabetes, and the results are shown in Table 1. The morbidity of TB patients with pre-diabetes is 12.4% (95 % CI 7,3%-17,5 %), and the morbidity of TB patients with diabetes is 13,3 % (95 % CI 7,9 %-18,7 %).
| Group (n=404) | Case number | Morbidity | 95 % CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| TB | 296 | ||
| TB+Pre-D | 50 | 12,4 % | 7,3 %-17,5 % |
| TB+D | 58 | 14,4 % | 7,9 %-18,7 % |
Notes: TB represents single TB patients, TB+Pre-D represents TB patients combined pre-diabetes, and TB+D represents TB patients combined diabetes.
Discussion
|
 |
 |
TB is a major public health threat in the world, nearly a third people infected by mycobacterium TB, and the numbers still develop with a 9,4 million increase every year. When confronted with TB, a chronic and long term illness, households face not only a physical and mental burden, but also an economic burden, which commonly includes the direct costs of treatment, medicine, informal payments, and the indirect costs of a reduction in their ability to generate income [8], especially in low- and middle-income countries. The prevention of TB relies mainly on early identification, prevention of latent TB infection reactivation, and infection control measures [9]. In this study, the data show that prevalence of TB patients in Heilongjiang province increase gradually from 2001-2011, so the trend of Pulmonary TB, the most important composition of TB.
Diabetes is also a chronic disease with a develop people suffering from it. The prevalence of diabetes usually occur with territoriality due to development of economic, custom of living or eating. The rising prevalence of diabetes thus poses an increasing risk for the control and prevention of TB [10]. As such, while this case study is focused on a single city in a developing health care system. TB and diabetes have strong co-morbidities, with both the incidence and severity of being affected by each other [11, 12], the causes are still not completely known. We performed this population-based study to investigate morbidity rates of pre-diabetes or diabetes in TB patients, thus provide a theoretical basis data for further exploring the interaction between TB and diabetes.
In this study, the morbidity of TB patients with pre-diabetes is 12,4 % (95 % CI 7,3 %-17,5 %), and the standardized rate is 15,0 %, which is 9,7 % higher than China's domestic normal population in 2010 [6], 3,75 % higher than the community population in Nangang district of Harbin in Heilongjiang province in 2009, suggesting TB facilitate the occurrence of pre-diabetes. Meanwhile, the morbidity of TB patients with diabetes is 14,4 % (95 % CI 7,9-18,7 %) in our study, and the standardized rate is 12,6 %, within the higher level of normal incidence (2 %-12,9 %) [13, 14]. In addition, this morbidity is also higher than 10,21 % from the community population in Nangang district of Harbin in Heilongjiang province in 2009, further indicating TB facilitate the occurrence of diabetes.
Total 255 TB patients, 60,6 % of the whole accounted for survey, are investigated with the age from 24~60 years old. Among them, there are 106 TB patients combined pre-diabetes and diabetes, and 73 patients are the age of 24~60 years old, which is a high percentage (67,6 %) of total cases in study. Therefore, we should focus on the publicity and education of synergy diseases for the patients aged from 24~60 years old, further to decrease the morbidity of synergy diseases.
Currently, new therapy is urgently need to treat the combination diseases between TB and diabetes, and people have tried many methods. It is said that application of IFNs play a supporting role for treatment of patients with refractory multiple drug-resistant TB combined diabetes, besides antibiotic treatment [15]. And our study preliminarily analyze the links between TB and diabetes, this association may provide a new strategy concerning the prevention and treatment of both diseases. In conclusion, our study suggest that the prevalence rate of TB patients suffering from pre-diabetes or diabetes is higher than general people.
Acknowledgments
|
 |
 |
This work was supported by grants from the special fund of translational medicine research center project (CR201406), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (81402267).
Literature |
 |
 1. Kapur A., Harries A.D. The double burden of diabetes and tuberculosis - public health implications // Diabetes Res Clin Pract. - 2013. - Vol. 101, № 1. - P. 10-9.
1. Kapur A., Harries A.D. The double burden of diabetes and tuberculosis - public health implications // Diabetes Res Clin Pract. - 2013. - Vol. 101, № 1. - P. 10-9. 2. Young F., et al. Increased risk of tuberculosis disease in people with diabetes mellitus: record-linkage study in a UK population // J. Epidemiol Community Health. - 2012. - Vol. 66, № 6. - P. 519-23.
2. Young F., et al. Increased risk of tuberculosis disease in people with diabetes mellitus: record-linkage study in a UK population // J. Epidemiol Community Health. - 2012. - Vol. 66, № 6. - P. 519-23. 3. Marais B.J., et al. Tuberculosis comorbidity with communicable and non-communicable diseases: integrating health services and control efforts // Lancet Infect Dis. - 2013. - Vol. 13, № 5. - P. 436-48.
3. Marais B.J., et al. Tuberculosis comorbidity with communicable and non-communicable diseases: integrating health services and control efforts // Lancet Infect Dis. - 2013. - Vol. 13, № 5. - P. 436-48. 4. Sulaiman S.A., et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes of tuberculosis patients in tertiary care setup // Am J Med Sci. - 2013. - Vol. 345. - № 4. - P. 321-5.
4. Sulaiman S.A., et al. Impact of diabetes mellitus on treatment outcomes of tuberculosis patients in tertiary care setup // Am J Med Sci. - 2013. - Vol. 345. - № 4. - P. 321-5. 5. Kang Y.A., et al. Impact of diabetes on treatment outcomes and long-term survival in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis // Respiration. - 2013. - Vol. 86, № 6. - P. 472-8.
5. Kang Y.A., et al. Impact of diabetes on treatment outcomes and long-term survival in multidrug-resistant tuberculosis // Respiration. - 2013. - Vol. 86, № 6. - P. 472-8. 6. Yang W., et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China // N Engl J Med. - 2010. - Vol. 362, № 12. - P. 1090-101.
6. Yang W., et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China // N Engl J Med. - 2010. - Vol. 362, № 12. - P. 1090-101. 7. Jingbo Zhao Y.Z., Shiying Fu, Fuman Wang, Liting Yang Cross-sectional study of impaired fasting glucose or diabetes in community residents of Nangang district of Harbin // Chinese journal of epidemiology. - 2009. - Vol. 30, № 2. - P. 110-114.
7. Jingbo Zhao Y.Z., Shiying Fu, Fuman Wang, Liting Yang Cross-sectional study of impaired fasting glucose or diabetes in community residents of Nangang district of Harbin // Chinese journal of epidemiology. - 2009. - Vol. 30, № 2. - P. 110-114. 8. Russell S. The economic burden of illness for households in developing countries: a review of studies focusing on malaria, tuberculosis, and human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome // Am J Trop Med Hyg. - 2004. - Vol. 71, № 2. - P. 147-55.
8. Russell S. The economic burden of illness for households in developing countries: a review of studies focusing on malaria, tuberculosis, and human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome // Am J Trop Med Hyg. - 2004. - Vol. 71, № 2. - P. 147-55. 9. Lee H., et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay for screening arthritis patients for latent tuberculosis infection before starting anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment // PLoS One. - 2015. - Vol. 10, № 3. - P. e0119260.
9. Lee H., et al. QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-Tube assay for screening arthritis patients for latent tuberculosis infection before starting anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment // PLoS One. - 2015. - Vol. 10, № 3. - P. e0119260. 10. Odone A., et al. The effect of diabetes and undernutrition trends on reaching 2035 global tuberculosis targets // Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. - 2014. - Vol. 2, № 9. - P. 754-64.
10. Odone A., et al. The effect of diabetes and undernutrition trends on reaching 2035 global tuberculosis targets // Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. - 2014. - Vol. 2, № 9. - P. 754-64. 11. Dooley K.E., Chaisson R.E. Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: convergence of two epidemics // Lancet Infect Dis. - 2009. - Vol. 9, № 12. - P. 737-46.
11. Dooley K.E., Chaisson R.E. Tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: convergence of two epidemics // Lancet Infect Dis. - 2009. - Vol. 9, № 12. - P. 737-46. 12. Jeon C.Y., Murray M.B. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of active tuberculosis: a systematic review of 13 observational studies // PLoS Med. - 2008. - Vol. 5, № 7. - P. e152.
12. Jeon C.Y., Murray M.B. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of active tuberculosis: a systematic review of 13 observational studies // PLoS Med. - 2008. - Vol. 5, № 7. - P. e152. 13. Ruslami R., et al. Implications of the global increase of diabetes for tuberculosis control and patient care // Trop Med Int Health. - 2010. - Vol. 15, № 11. - P. 1289-99.
13. Ruslami R., et al. Implications of the global increase of diabetes for tuberculosis control and patient care // Trop Med Int Health. - 2010. - Vol. 15, № 11. - P. 1289-99. 14. Pan C., et al. Burden of diabetes in the adult Chinese population: A systematic literature review and future projections // Int J Gen Med. - 2010. - № 3. - P. 173-9.
14. Pan C., et al. Burden of diabetes in the adult Chinese population: A systematic literature review and future projections // Int J Gen Med. - 2010. - № 3. - P. 173-9. 15. Zarogoulidis P., et al. The effect of combination IFN-alpha-2a with usual antituberculosis chemotherapy in non-responding tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the literature // J Chemother. - 2012. - Vol. 24, № 3. - P. 173-7.
15. Zarogoulidis P., et al. The effect of combination IFN-alpha-2a with usual antituberculosis chemotherapy in non-responding tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus: a case report and review of the literature // J Chemother. - 2012. - Vol. 24, № 3. - P. 173-7.
Телефон: (4212) 76-13-96
«Дальневосточный медицинский журнал»

